Understanding DC & BO Motors: Types, Working, and Applications

You would be surprised to know how many electric motors are there in the room you are sitting in right now.
Are you sitting under the comfort of a fan or an AC? There are motors inside. Toys, washing machine, mixer grinder, hand blender, cars, aeroplanes, trains, motorcycles, scooters and even the laptop you’re reading this on, has a motor. You name it and you find a motor there.
Electric motors are one of the finest inventions of the nineteenth century. They are the magical little things that harness the power of electricity and make things move!
It’s only fair to learn how such an important machine works.
What is a motor?
A motor is like a magic machine that turns electricity into motion! It’s that little thing that spins things around, like the wheels of your robotic car, the blades of a fan, or the drum in your washing machine.
When you give it electricity, it says, “Let’s go!” and starts spinning, making all kinds of cool stuff rotate. Without motors, our world would be way less fun (and way more tiring)!
Who invented electric motors?
Many times scientific inventions are based on principles set by previous scientists. Same applies to the invention of motors. Many scientists have worked and given principles and demonstrations.
Michael Faraday is noted as the first to demonstrate the working model of rotary motion using electricity in 1821.
Then in 1832, William Sturgeon developed the first prototype of working DC motor. Which Thomas Devenport converted into a commercially viable model in 1834.
Charles Schenk Bradley, Nikola Tesla and Mikhail Dolivo-Dobrovolsky separately developed AC motors in their own way.

What are the types of motors?
Motors can be classified by soooo many parameters in various categories and subcategories, but let’s keep “Our Kaam se Kaam”.
The motors which are powered by Alternating Current – AC are called AC motors. AC means the power that we receive in our switchboards. Motor in the Fan is an AC motor.
The motor which operates on Direct Current – DC is called DC motors. The power supply from clock cells or Havi’s power bank is DC. Motors that we have in Robotics Kit boxes are DC motors.
DC motors again can be of a variety of types according to the purpose they are meant for.
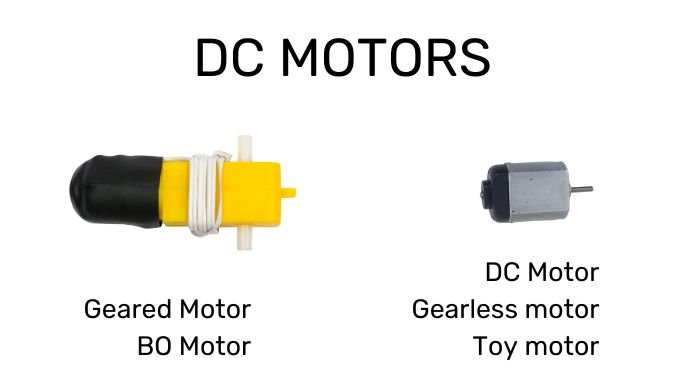
There are two types of DC motors in the Robotics kit for beginners.
This tiny motor is known as DC motor, Gearless motor, and Toy motor. This is one of the simplest motor being used mostly in all sorts of toys hence it is known as toy motor. You call it toy motor but it can do wonders. Make a few creations with it and then only you know.
This yellow DC motor is known as BO motor and Geared motor.
What is a BO motor?
A BO motor is a small, lightweight, and low-cost DC motor commonly used in robotics and hobby projects. The name “BO” stands for Battery Operated because these motors are designed to run on small batteries (like 3V to 12V), making them perfect for simple DIY applications.
So yes, technically speaking, a toy motor is also a BO motor.
What is the difference between geared motor and gearless motor?
Which of these two do you think is better?
Let’s do a series of experiments to understand and answer this.
Make the Power – Motor – Motor circuit using Havi Elements.

Connect a geared motor with one of the motor elements and gearless motor with the other.
Observe the speed of the shaft of both.
Which one is faster? Geared motor (BO motor as per conventional name, the yellow one) or gearless motor (Toy motor, DC motor as per conventional name)?
You will feel that the gearless motor is faster.
Now, try to hold the shaft of the geared motor. Can you hold and stop it easily from rotating? Do the same experiment with a gearless motor.
Which one is easy to stop with your fingers? Yes, gearless. The Geared motor is stubborn it seems!
So a DC motor’s performance can be measured on two parameters: speed and power.
Toy DC motor is speedier but has less power, you can stop it easily and even if you try rotating the shaft while the power is off, you would be able to do it easily.
The BO motor has more power. It rotates slowly but is hard to stop.
That power is known as torque in technical terms.
Now you can do another experiment. Attach a wheel with a Geared motor shaft. Try to attach the wheel with a gearless motor’s shaft, though not easy. You can get help with a piece of DST. Turn the power on. Both the wheels will start rotating. Now touch the wheels one by one with your one finger and try to stop the wheel by pressing. See what force you need to apply to stop them.
We have a question for you. In real cars, which gear should be used when you want to climb a steep slope? Why?
Applications of Geared motors and DC Toy motor
Geared and gearless have specific applications. When you need more power, for example the spinning tray of a microwave, which is supposed to rotate with a load of food on it, you have to use Geared motors, the BO motors.
When you need less power but more speed, like a fan, or Newton’s Disc project, you need to use a gearless motor. Even in Drones.
Unit to measure the speed of a BO motor
A BO motor can be measured with the unit called RPM. What’s RPM? That’s Revolution Per Minute. It indicates how many complete turns the shaft makes in one minute.
Higher the RPM = higher the speed but lower the torque
Lower the RPM = lower the speed but higher the torque
Revolution per minute or Rotation per minute?
A quirky question. When something spins around its own axis we call it rotation, right? Earth’s rotation. Then why is the movement of the shaft termed with revolution?
See, when an object is spinning around its own axis, we call it Rotation. And when the object is spinning around another object we call it Revolution.
Now here you might think the motor shaft is rotating and not revolving. But remember that the motor itself is not rotating! Here the shaft, the axle is spinning and in a 360 degree circle. People who defined the terms just chose to use the respective terms of earth and motor.
So there is no completely justifiable answer why we use rotation for earth and revolution for motors. Just like that.
English is a funny language!
How DC motor works?
Let’s open up a DC motor to understand how a motor works.




As you know opposite poles of a magnet attract and similar poles repel.
North South – Attraction
South North – Attraction
North North – Repulsion
South South – Repulsion


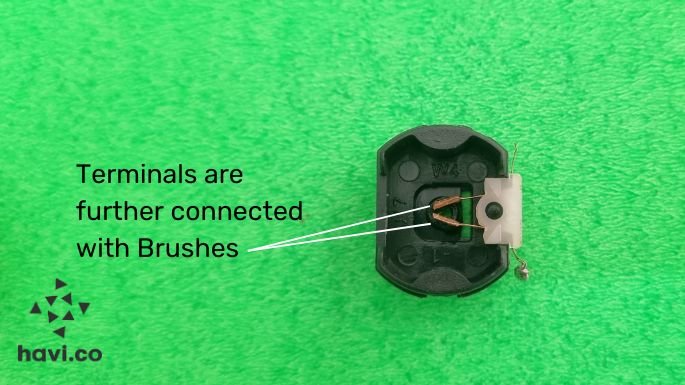
- Brushes will pass the current to the commutator.
- Because of the electricity, the armature coil turns into a temporary magnet.
- Attraction and repulsion between static magnets and temporary magnets will cause the armature to rotate a bit, say halfway! And it should stop there as poles of all the magnets are in the correct position, with no more repulsion.
- But our commutator bro has a slit if you remember. Yes, they are two bros. As the armature rotates, the commutator too rotates. That alters the current. One which was Positive earlier now receives negative and vice versa. That causes armature coils too, change their polarity. The north pole becomes south and vice versa.
- So the love-hate relationship between static magnets and temporary magnets keeps going and that keeps armature spinning.
- Now a suspense to reveal, there are not two bros but three. Yes three commutator pieces are there and three armature coils as well. The third one is to fill any gap in between.It makes sure the armature keeps moving without even a minor gap. And you know in more powerful motors there would be many more armatures and commutators.
That’s how electromagnetism causes motor shaft spinning and the entire world moving, your robotic car too!
How BO motor works
BO motor or Geared motor has a DC motor in it. The motor axle has a bearing on it. The bearing further is connected with a gearbox that rotates the shaft we see outside. With that shaft we attach the wheels!
How do we change the direction of the motor?
You have this switch on the motor element. When you toggle the switch it swaps the supply to the terminal. Positive becomes negative and vice versa. So everything changes and ultimately the direction of the armature too. Current has altered and everything now goes in the opposite direction. So the motor and the connected wheel go in the opposite direction.
Now you know that electric motors are fascinating inventions that have revolutionized the way we live and work. Whatever you build, motors are the hidden heroes making it all possible. By understanding how they work and experimenting with different types like DC and BO motors, you’re not just learning—you’re opening the door to a world of endless possibilities. So, what will you create next with your geared and gearless motors?
Also Read

